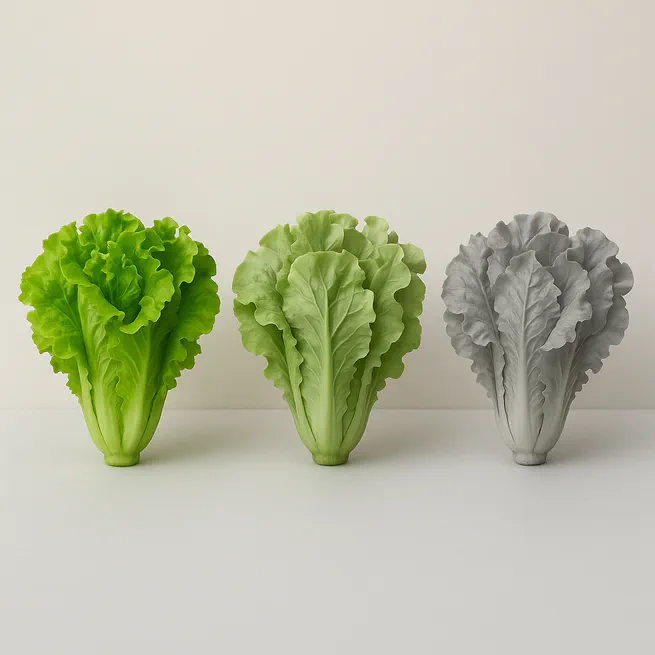

The colour of food serves as a highly salient visual cue, helping us to assess its freshness and quality. In Experiment 1, we investigated how partial and complete (i.e., greyscale) desaturation of food images influenced explicit evaluations of perishable and preserved food items. We found that both self-reported cravings and perceived palatability decreased with decreasing image saturation, with larger effects observed for perishable food items compared to preserved ones. These results suggest that colour plays an important role in food evaluation, especially for perishable items, which may rely more heavily on visual cues of freshness. Furthermore, previous research has shown that attentional biases towards food images are eliminated when the images are grey-scaled. However, it remains unclear whether colour desaturation also affects behavioural/motivational responses, such as approach biases. To address this, we conducted Experiments 2 and 3, using a stimulus-response compatibility task to assess the influence of colour desaturation on approach behaviour towards perishable and preserved food images. Contrary to the previous findings on attentional biases, we observed robust approach biases for all food images, with no significant differences across saturation conditions or food types. Our findings suggest that while attentional biases are sensitive to low-level perceptual features, such as colour saturation, approach biases may be less influenced by variations in perceptual stimulus properties. This implies that motivational approach responses are primarily driven by learned associations with food rewards rather than basic stimulus saliency, highlighting a potential dissociation between attentional and motivational processes in healthy eaters.
Sep 24, 2025
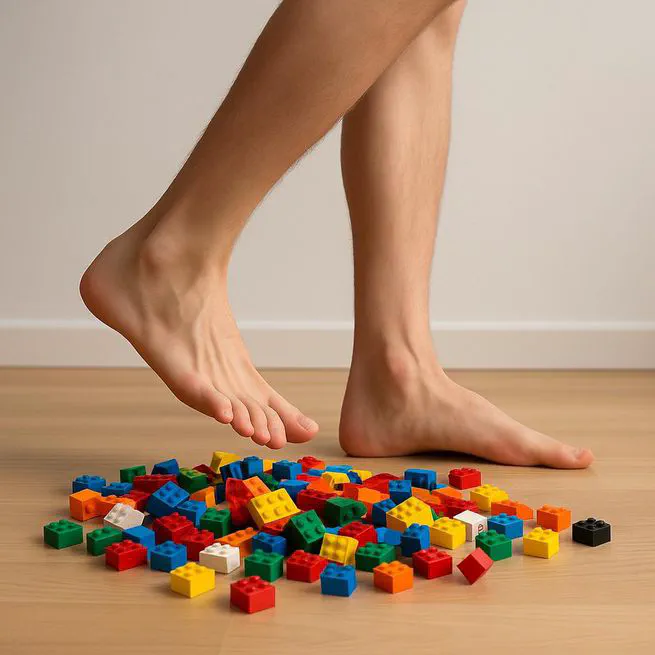

Stepping over obstacles requires adjusting the foot trajectory to avoid contact with surfaces that may be hazardous or unpleasant to step on. While it is well established that obstacle height and stability influence stepping behaviour, little is known about how perceptual affective evaluations, such as dangerousness, unpleasantness, and painfulness, modulate avoidance strategies. In Experiment 1 (N = 20), participants stepped over obstacles covered with stones varying in size and density while rating their perceived unpleasantness. Visual uncertainty was manipulated by comparing monocular and binocular viewing. Lead minimum foot clearance (MFC) was initially higher under monocular vision but decreased to binocular levels over trials. While obstacle unpleasantness did not systematically affect MFC or crossing step length, perceived unpleasantness ratings correlated weakly with crossing step length. However, because dangerousness and painfulness ratings were not collected, it remained unclear whether unpleasantness directly influenced avoidance behaviour or served as a proxy for perceived risk. To address this, Experiment 2 (N = 22) introduced obstacles covered with metal stud spikes or smooth surfaces, with additional ratings of dangerousness and painfulness. Results showed that MFC was higher for spiky than smooth obstacles. Crucially, in this experiment, ratings of perceived dangerousness, not unpleasantness, correlated positively with crossing step length, after controlling for other perceptual ratings. These findings suggest that perceptual affective properties modulate avoidance parameters. However, the nature of those modulations is stimulus specific and highly depends on task demands.
Aug 10, 2025
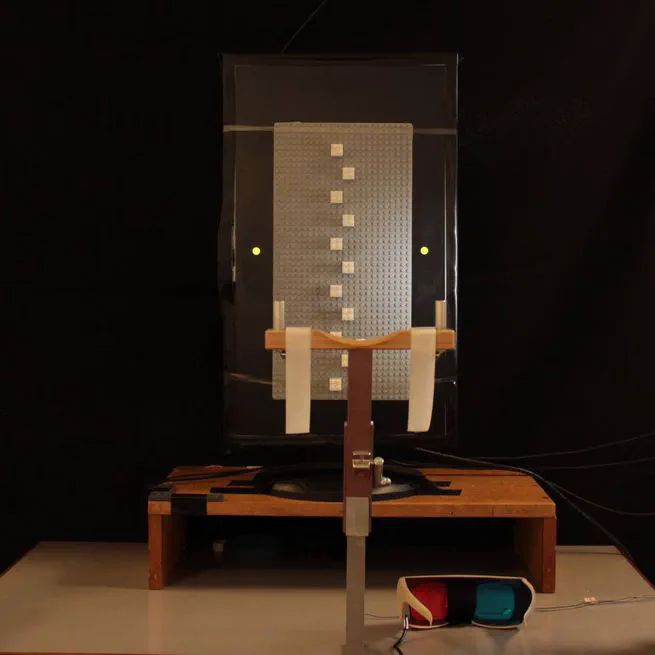
Simulated environments, e.g., virtual or augmented reality environments, are becoming increasingly popular for the investigation and training of motor actions. Yet, so far it remains unclear if results of research and training in those environments transfer in the expected way to natural environments. Here, we investigated the types of visual cues that are required to ensure naturalistic hand movements in simulated environments. We compared obstacle avoidance of physical objects with obstacle avoidance of closely matched 2D and 3D images of the physical objects. Participants were asked to reach towards a target position without colliding with obstacles of varying height that were placed in the movement path. Using a pre-test post-test design, we tested obstacle avoidance for 2D and 3D images of obstacles both before and after exposure to the physical obstacles. Consistent with previous findings, we found that participants initially underestimated the magnitude differences between the obstacles, but after exposure to the physical obstacles avoidance performance for the 3D images became similar to performance for the physical obstacles. No such change was found for 2D images. Our findings highlight the importance of disparity cues for naturalistic motor actions in personal space. Furthermore, they suggest that the observed change in obstacle avoidance for 3D images resulted from a calibration of the disparity cues in the 3D images using an accurate estimate of the egocentric distance to the obstacles gained from the interaction with the physical obstacles.
Jun 1, 2025
Add the full text or supplementary notes for the publication here using Markdown formatting.
Jan 1, 2024
Add the full text or supplementary notes for the publication here using Markdown formatting.
Jan 1, 2024
Add the full text or supplementary notes for the publication here using Markdown formatting.
Jan 1, 2023
Add the full text or supplementary notes for the publication here using Markdown formatting.
Jan 1, 2023
Add the full text or supplementary notes for the publication here using Markdown formatting.
Jan 1, 2023
Add the full text or supplementary notes for the publication here using Markdown formatting.
Jan 1, 2022
Add the full text or supplementary notes for the publication here using Markdown formatting.
Jan 1, 2022